Using the Vector Type
MPI_Type_vector enables the definition of non-contiguous vectors with constant stride. Where might you use it?
One possible scenario is in a datatype that corresponds to the rows of a Fortran matrix. In Fortran, due to column-major
ordering, row data are not contiguous. They skip nrows entries for every element. Therefore the stride
parameter naturally equals nrows:
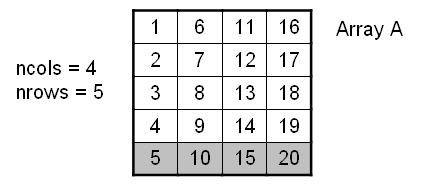
! Fortran code to create vtype, an MPI row datatype for matrix A
call MPI_Type_vector(ncols,1,nrows,MPI_DOUBLE_PRECISION,vtype,ierr)
call MPI_Type_commit(vtype,ierr)
call MPI_Send(A(nrows,1),1,vtype...)
Notice that it takes two steps to create a derived datatype: a call to MPI_Type_*, followed by a call to MPI_Type_commit.
©
|
Cornell University
|
Center for Advanced Computing
|
Copyright Statement
|
Access Statement
CVW material development is supported by NSF OAC awards 1854828, 2321040, 2323116 (UT Austin) and 2005506 (Indiana University)
CVW material development is supported by NSF OAC awards 1854828, 2321040, 2323116 (UT Austin) and 2005506 (Indiana University)