File Views
A file view is a triplet of arguments (displacement, etype, filetype) that is passed to MPI_File_set_view.
- displacement = number of bytes to be skipped from the start of the file
- etype = unit of data access (can be any basic or derived datatype)
- filetype = specifies layout of etypes within the file
Note that etype is considered to be the elementary type, but since it can be a derived datatype, there’s really nothing elementary about it. In fact, file views are often varined in terms of MPI derived types, a subject which is covered in the MPI Advanced Topics roadmap.
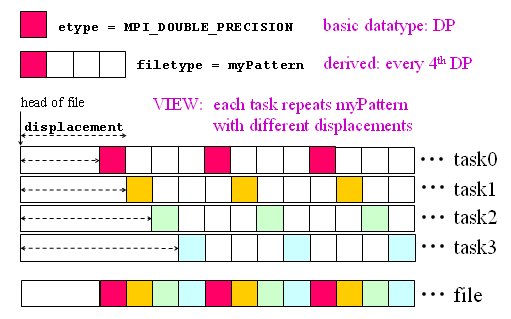
In the file view depicted below, etype is double precision, filetype is a vector type, and displacement is used to stagger the starting positions by MPI rank. Specifically, the displacement for a given MPI rank is base+rank*size(1.d0) in Fortran, or base+rank*sizeof(double) in C; this becomes the starting point for the filetype myPattern, for each rank.
CVW material development is supported by NSF OAC awards 1854828, 2321040, 2323116 (UT Austin) and 2005506 (Indiana University)