Two Ways to Broadcast
Example of two ways (simple way, better way) to do a broadcast.
Simple approach
One process broadcasts the same message to all the other processes, one at a time.
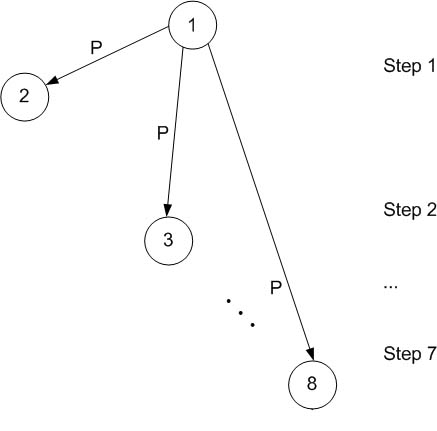
| Amount of data transferred | \((N-1)*p\) |
|---|---|
| Number of processes | \(N\) |
| Size of message | \(p\) |
| Number of steps | \(N-1\) |
Smarter approach
Let other processes help propagate the message. In the first step, process 1 sends the message to process 2. In the second step, both processes can now participate: process 1 sends to process 3, while process 2 sends to process 4. Similarly, by the third step, four processes (1, 3, 2, and 4) are sending the message to the four remaining processes (5, 6, 7, and 8).
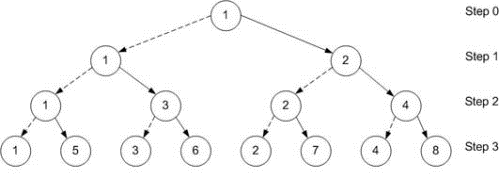
| Amount of data transferred | \((N-1)*p\) |
|---|---|
| Number of processes | \(N\) |
| Size of message | \(p\) |
| Number of steps | \(\log_2 N\) |
Compare the number of steps in the two approaches:
- Simple approach: \(N-1\)
- Smarter approach: \(\log_2 N\)
The latter scales better as N increases.
©
|
Cornell University
|
Center for Advanced Computing
|
Copyright Statement
|
Access Statement
CVW material development is supported by NSF OAC awards 1854828, 2321040, 2323116 (UT Austin) and 2005506 (Indiana University)
CVW material development is supported by NSF OAC awards 1854828, 2321040, 2323116 (UT Austin) and 2005506 (Indiana University)