Forward Mode Automatic Differentiation
Forward mode AD computes derivatives by propagating derivative information forward through the computational graph, following the same path as the function evaluation.
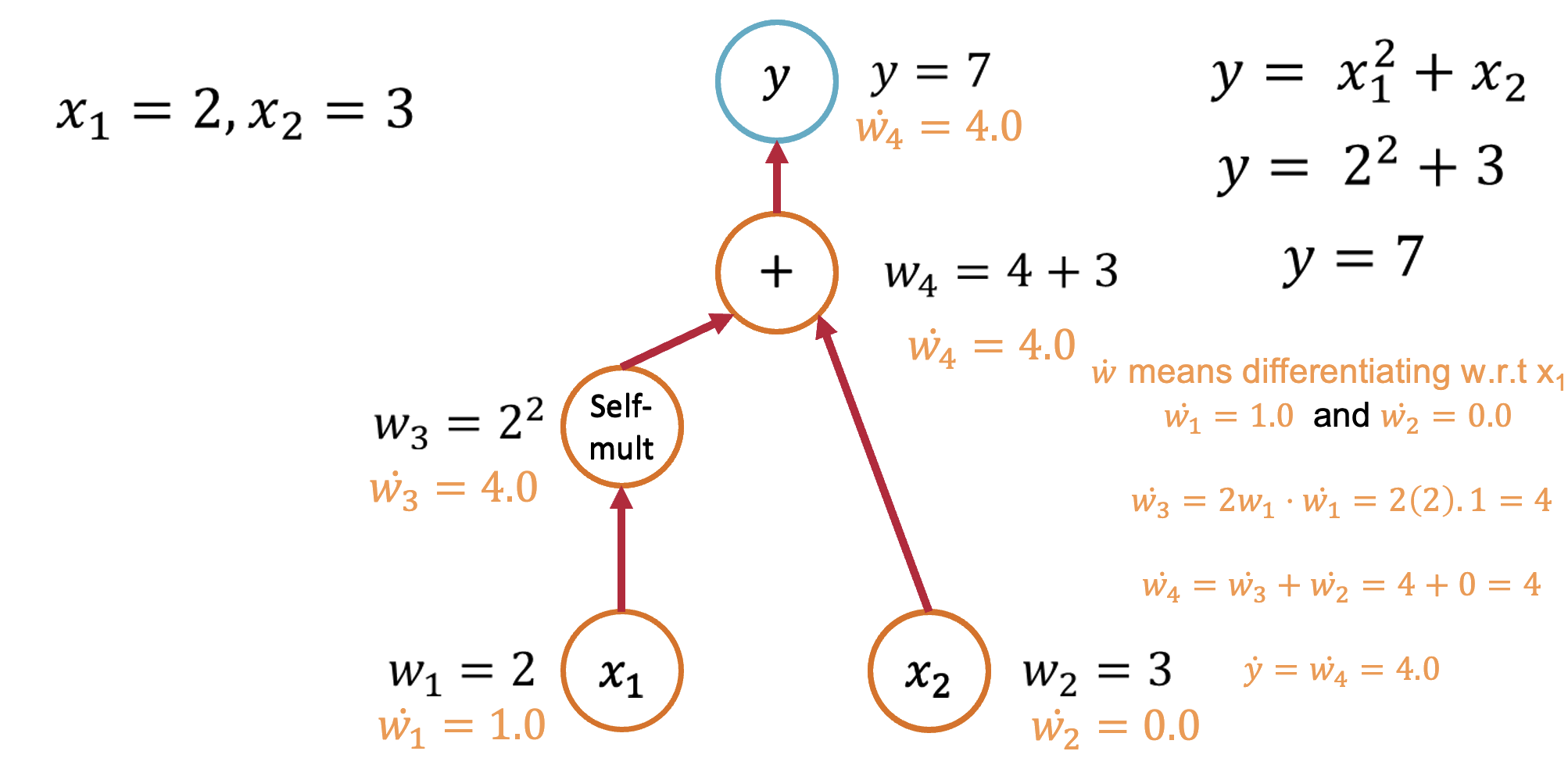
Forward Mode: Computing \(\frac{\partial y}{\partial x_1}\)
Starting with our function \(y = x_1^2 + x_2\), let's trace through the computation:
- Seed the input: Set \(\dot{x}_1 = 1\) and \(\dot{x}_2 = 0\) (we're differentiating w.r.t. \(x_1\))
- Forward propagation:
- \(v_1 = x_1^2\), so \(\dot{v}_1 = 2x_1 \cdot \dot{x}_1 = 2x_1 \cdot 1 = 2x_1\)
- \(y = v_1 + x_2\), so \(\dot{y} = \dot{v}_1 + \dot{x}_2 = 2x_1 + 0 = 2x_1\)
- Result: \(\frac{\partial y}{\partial x_1} = 2x_1\)
Forward Mode: Computing \(\frac{\partial y}{\partial x_2}\)
To get the derivative w.r.t. \(x_2\), we seed differently:
- Seed the input: Set \(\dot{x}_1 = 0\) and \(\dot{x}_2 = 1\)
- Forward propagation:
- \(v_1 = x_1^2\), so \(\dot{v}_1 = 2x_1 \cdot \dot{x}_1 = 2x_1 \cdot 0 = 0\)
- \(y = v_1 + x_2\), so \(\dot{y} = \dot{v}_1 + \dot{x}_2 = 0 + 1 = 1\)
- Result: \(\frac{\partial y}{\partial x_2} = 1\)
Key Insight:
Forward mode requires one pass per input variable to compute all partial derivatives.
©
|
Cornell University
|
Center for Advanced Computing
|
Copyright Statement
|
Access Statement
CVW material development is supported by NSF OAC awards 1854828, 2321040, 2323116 (UT Austin) and 2005506 (Indiana University)
CVW material development is supported by NSF OAC awards 1854828, 2321040, 2323116 (UT Austin) and 2005506 (Indiana University)